NASA / JPL
NASA's Opportunity Rover Mission on Mars Comes to End (News Release)
NASA / JPL
NASA's Opportunity Rover Mission on Mars Comes to End (News Release)
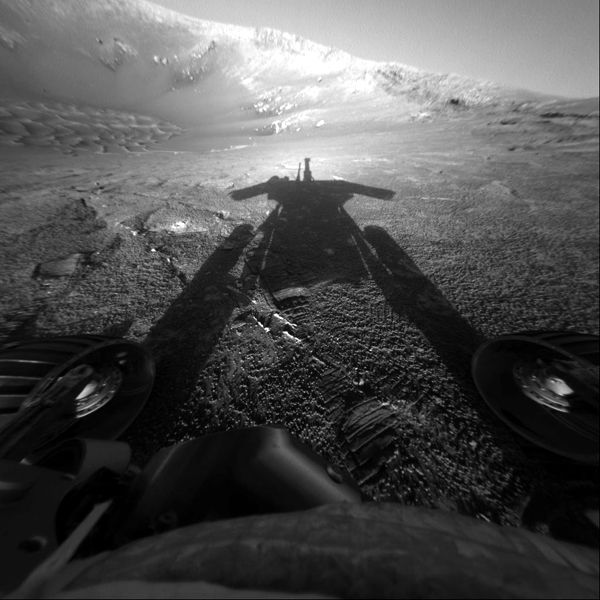
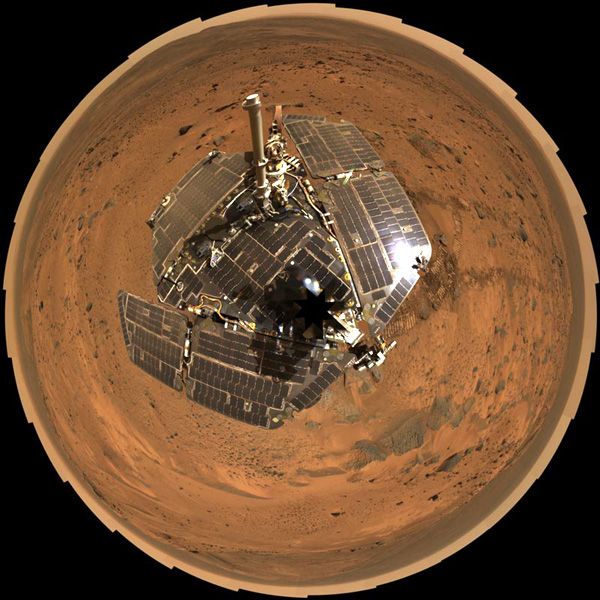
One of the most successful and enduring feats of interplanetary exploration, NASA's
Opportunity rover mission is at an end after almost 15 years exploring the surface of Mars and helping lay the groundwork for NASA's return to the Red Planet.
The Opportunity rover stopped communicating with Earth when a severe Mars-wide dust storm blanketed its location in June 2018. After more than a thousand commands to restore contact, engineers in the Space Flight Operations Facility at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory
(JPL) made their last attempt to revive Opportunity Tuesday, to no avail. The solar-powered rover's final communication was received June 10.
"It is because of trailblazing missions such as Opportunity that there will come a day when our brave astronauts walk on the surface of Mars," said NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine. "And when that day arrives, some portion of that first footprint will be owned by the men and women of Opportunity, and a little rover that defied the odds and did so much in the name of exploration."
Designed to last just 90 Martian days and travel 1,100 yards
(1,000 meters), Opportunity vastly surpassed all expectations in its endurance, scientific value and longevity. In addition to exceeding its life expectancy by 60 times, the rover traveled more than 28 miles
(45 kilometers) by the time it reached its most appropriate final resting spot on Mars - Perseverance Valley.
"For more than a decade, Opportunity has been an icon in the field of planetary exploration, teaching us about Mars' ancient past as a wet, potentially habitable planet, and revealing uncharted Martian landscapes," said Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA's Science Mission Directorate. "Whatever loss we feel now must be tempered with the knowledge that the legacy of Opportunity continues - both on the surface of Mars with the
Curiosity rover and
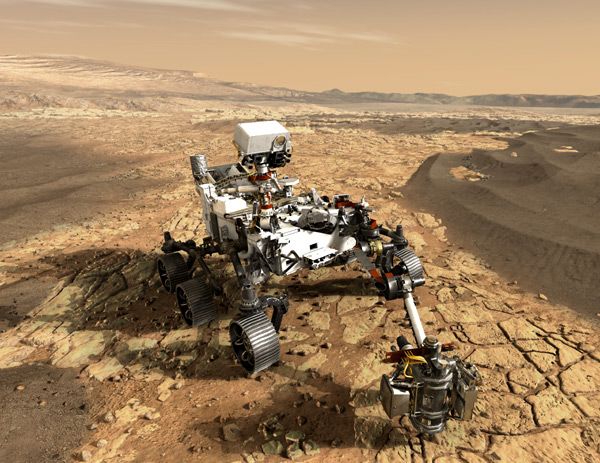
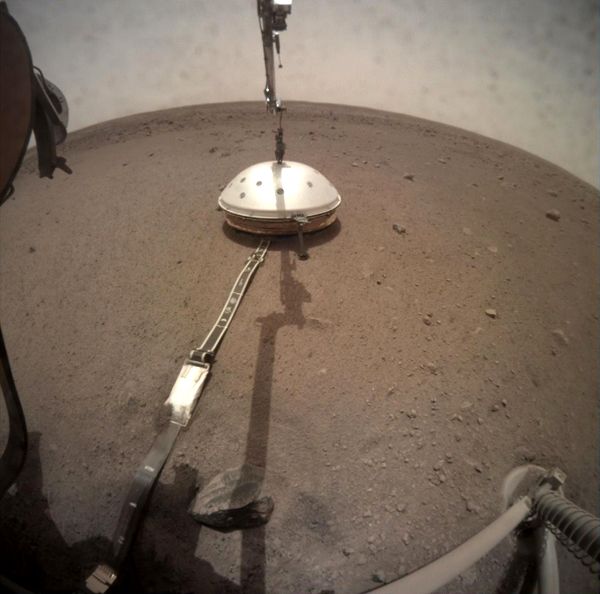
InSight lander - and in the clean rooms of JPL, where the upcoming
Mars 2020 rover is taking shape."
The final transmission, sent via the 70-meter Mars Station antenna at NASA's Goldstone Deep Space Complex in California, ended a multifaceted, eight-month recovery strategy in an attempt to compel the rover to communicate.
"We have made every reasonable engineering effort to try to recover Opportunity and have determined that the likelihood of receiving a signal is far too low to continue recovery efforts," said John Callas, manager of the
Mars Exploration Rover (MER) project at JPL.
Opportunity landed in the Meridiani Planum region of Mars on Jan. 24, 2004, seven months after its launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Its twin rover,
Spirit, landed 20 days earlier in the 103-mile-wide
(166-kilometer-wide) Gusev Crater on the other side of Mars. Spirit logged almost 5 miles
(8 kilometers) before its mission wrapped up in May 2011.
From the day Opportunity landed, a team of mission engineers, rover drivers and scientists on Earth collaborated to overcome challenges and get the rover from one geologic site on Mars to the next. They plotted workable avenues over rugged terrain so that the 384-pound
(174-kilogram) Martian explorer could maneuver around and, at times, over rocks and boulders, climb gravel-strewn slopes as steep as 32-degrees
(an off-Earth record), probe crater floors, summit hills and traverse possible dry riverbeds. Its final venture brought it to the western limb of Perseverance Valley.
"I cannot think of a more appropriate place for Opportunity to endure on the surface of Mars than one called Perseverance Valley," said Michael Watkins, director of JPL. "The records, discoveries and sheer tenacity of this intrepid little rover is testament to the ingenuity, dedication, and perseverance of the people who built and guided her."
More Opportunity Achievements
- Set a one-day Mars driving record March 20, 2005, when it traveled 721 feet (220 meters).
- Returned more than 217,000 images, including 15 360-degree color panoramas.
- Exposed the surfaces of 52 rocks to reveal fresh mineral surfaces for analysis and cleared 72 additional targets with a brush to prepare them for inspection with spectrometers and a microscopic imager.
- Found hematite, a mineral that forms in water, at its landing site.
- Discovered strong indications at Endeavour Crater of the action of ancient water similar to the drinkable water of a pond or lake on Earth.
All of the off-roading and on-location scientific analyses were in service of the Mars Exploration Rovers' primary objective: To seek out historical evidence of the Red Planet's climate and water at sites where conditions may once have been favorable for life. Because liquid water is required for life, as we know it, Opportunity's discoveries implied that conditions at Meridiani Planum may have been habitable for some period of time in Martian history.
"From the get-go, Opportunity delivered on our search for evidence regarding water," said Steve Squyres, principal investigator of the rovers' science payload at Cornell University. "And when you combine the discoveries of Opportunity and Spirit, they showed us that ancient Mars was a very different place from Mars today, which is a cold, dry, desolate world. But if you look to its ancient past, you find compelling evidence for liquid water below the surface and liquid water at the surface."
All those accomplishments were not without the occasional extraterrestrial impediment. In 2005 alone, Opportunity lost steering to one of its front wheels, a stuck heater threatened to severely limit the rover's available power, and a Martian sand ripple almost trapped it for good. Two years later, a two-month dust storm imperiled the rover before relenting. In 2015, Opportunity lost use of its 256-megabyte flash memory and, in 2017, it lost steering to its other front wheel.
Each time the rover faced an obstacle, Opportunity's team on Earth found and implemented a solution that enabled the rover to bounce back. However, the massive dust storm that took shape in the summer of 2018 proved too much for history's most senior Mars explorer.
"When I think of Opportunity, I will recall that place on Mars where our intrepid rover far exceeded everyone's expectations," Callas said. "But what I suppose I'll cherish most is the impact Opportunity had on us here on Earth. It's the accomplished exploration and phenomenal discoveries. It's the generation of young scientists and engineers who became space explorers with this mission. It's the public that followed along with our every step. And it's the technical legacy of the Mars Exploration Rovers, which is carried aboard Curiosity and the upcoming Mars 2020 mission. Farewell, Opportunity, and well done."
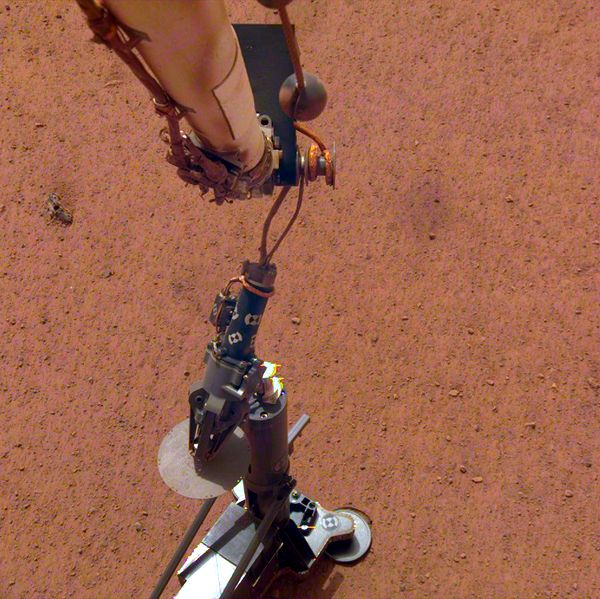
Mars exploration continues unabated. NASA's InSight lander, which touched down on Nov. 26, is just beginning its scientific investigations. The Curiosity rover has been exploring Gale Crater for more than six years. And, NASA's Mars 2020 rover and the European Space Agency's
ExoMars rover both will launch in July 2020, becoming the first rover missions designed to seek signs of past microbial life on the Red Planet.
JPL managed the Mars Exploration Rovers Opportunity and Spirit for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
Source: Jet Propulsion Laboratory
****
 NASA / JPL
NASA / JPL