USMC / Lockheed Martin
U.S. Marines Corps Declares the F-35B Operational (Press Release)
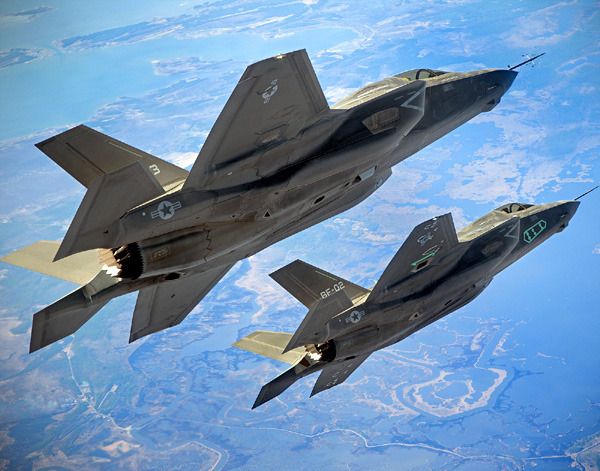
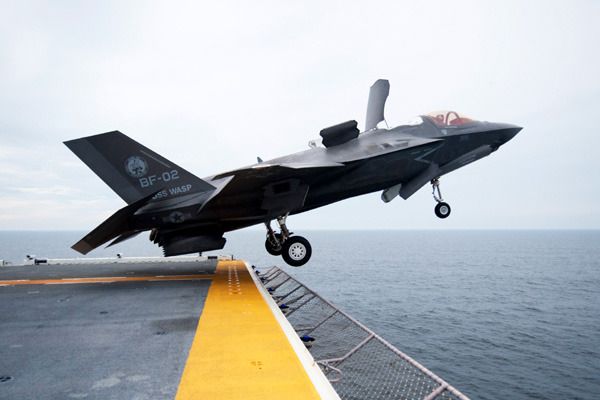
WASHINGTON -- The U.S. Marine Corps' F-35B Lightning II aircraft reached initial operational capability July 31, 2015 with a squadron of 10 F-35Bs ready for world-wide deployment.
Marine Fighter Attack Squadron 121 (VMFA-121), based in Yuma, Arizona, is the first squadron in military history to become operational with an F-35 variant, following a five-day Operational Readiness Inspection, which concluded July 17.
“I am pleased to announce that VMFA-121 has achieved Initial Operational Capability in the F-35B, as defined by requirements outlined in the June 2014 Joint Report to Congressional Defense Committees,” said Gen. Joseph Dunford, Commandant of the Marine Corps. “VMFA-121 has ten aircraft in the Block 2B configuration with the requisite performance envelope and weapons clearances, to include the training, sustainment capabilities, and infrastructure to deploy to an austere site or a ship. It is capable of conducting Close Air Support, Offensive and Defensive Counter Air, Air Interdiction, Assault Support Escort and Armed Reconnaissance as part of a Marine Air Ground Task Force, or in support of the Joint Force.”
Dunford stated that he has his full confidence in the F-35B’s ability to support Marines in combat, predicated on years of concurrent developmental testing and operational flying.
“Prior to declaring IOC, we have conducted flight operations for seven weeks at sea aboard an L-Class carrier, participated in multiple large force exercises, and executed a recent operational evaluation which included multiple live ordnance sorties," said Dunford. "The F-35B’s ability to conduct operations from expeditionary airstrips or sea-based carriers provides our Nation with its first 5th generation strike fighter, which will transform the way we fight and win.”
As the future of Marine Corps tactical aviation, the F-35 will eventually replace three legacy platforms: the AV-8B Harrier, the F/A-18 Hornet, and the EA-6B Prowler.
“The success of VMFA-121 is a reflection of the hard work and effort by the Marines in the squadron, those involved in the program over many years, and the support we have received from across the Department of the Navy, the Joint Program Office, our industry partners, and the Under Secretary of Defense. Achieving IOC has truly been a team effort,” concluded Dunford.
The U.S. Marine Corps has trained and qualified more than 50 Marine F-35B pilots and certified about 500 maintenance personnel to assume autonomous, organic-level maintenance support for the F-35B.
VMFA-121’s transition will be followed by Marine Attack Squadron 211 (VMA-211), an AV-8B squadron, which is scheduled to transition to the F-35B in fiscal year 2016. In 2018, VAM-311 will conduct its transition to the F-35B.
Source: United States Marine Corps
****

USMC / Lockheed Martin